-
Myths and Truths About Hearing Aids
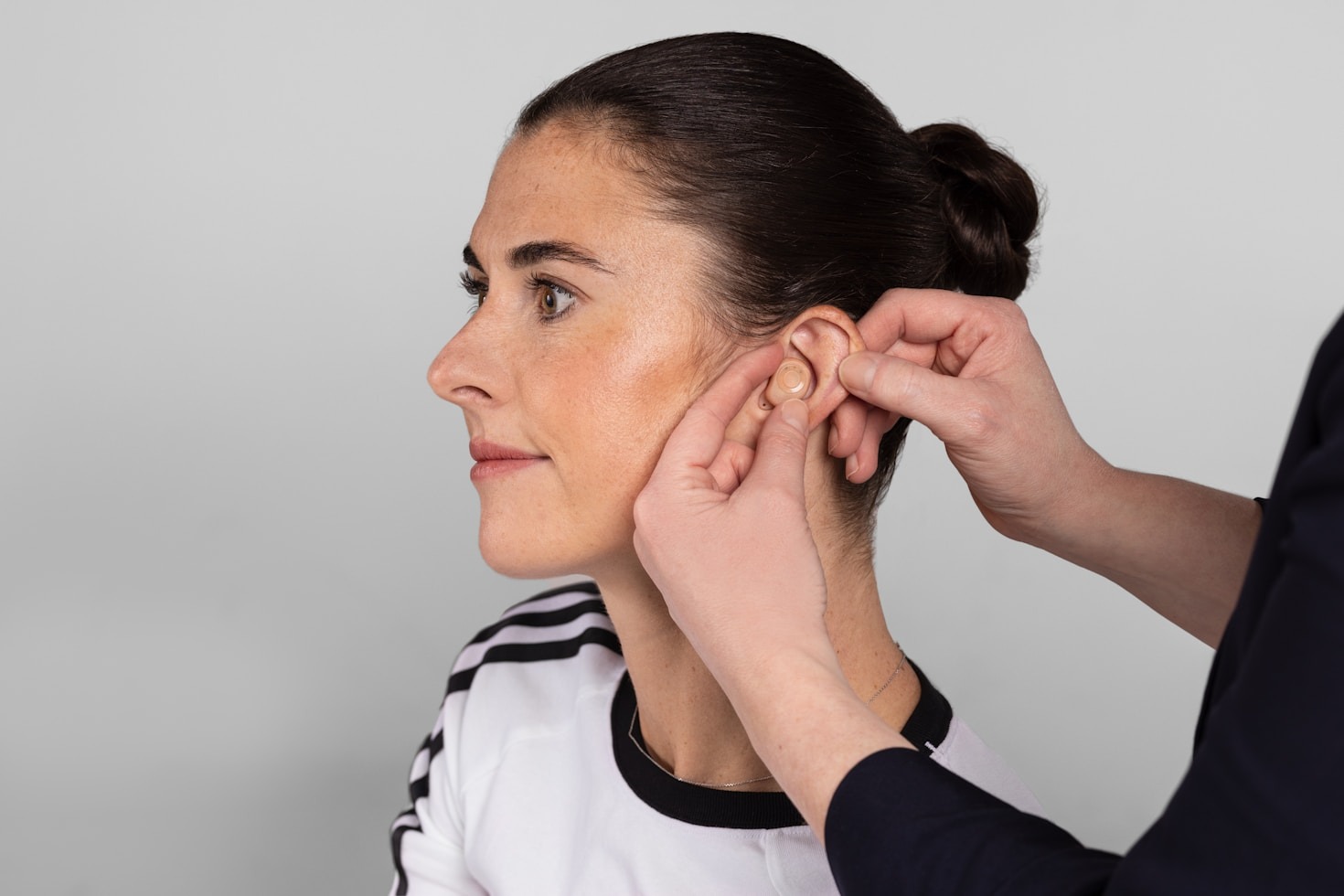
Myth: Hearing aids restore hearing to normal.
Truth: Hearing aids amplify sounds to improve hearing but do not cure hearing loss or restore hearing to normal levels.Myth: Hearing aids are only for elderly people.
Truth: People of all ages, including children and young adults, can benefit from hearing aids if they have hearing loss.Myth: Hearing aids are bulky and uncomfortable.
Truth: Modern hearing aids are small, lightweight, and designed for comfort and discreet wear.Myth: Hearing aids will make all sounds louder and overwhelming.
Truth: Hearing aids are programmed to amplify specific frequencies and reduce background noise, providing a clearer listening experience.Myth: You don’t need hearing aids if you can hear some sounds.
Truth: Even mild to moderate hearing loss can impact communication and quality of life, and early use of hearing aids can prevent further difficulties.Myth: Hearing aids are too expensive and not worth the investment.
Truth: While hearing aids can be costly, many options and financial assistance programs are available, and the benefits to communication and well-being are significant.Understanding these myths and truths helps individuals make informed decisions about hearing aids and encourages timely intervention for hearing loss.
Safe Listening Practices
Consistently practicing safe listening is key to preventing hearing loss. Recommendations from organizations like the World Health Organization include setting lower volume limits, using noise-canceling headphones instead of turning up the sound, taking breaks from noisy settings, and encouraging children and young adults to adopt these habits early.
Environmental and Occupational Controls
In workplaces, controlling noise at its source can be highly effective. Methods include regular maintenance of machinery, purchasing quieter equipment, using sound dampening materials, and providing thorough training on hearing protection. Fit-testing hearing protectors and conducting regular noise assessments also help ensure workers are protected.
Healthy Habits and Ear Care
Healthy habits play a crucial role in maintaining ear health and preventing hearing loss. Regularly cleaning the ears gently and avoiding the use of sharp objects can prevent damage to the ear canal and eardrum. Protecting ears from loud noises by using earplugs or noise-canceling headphones helps reduce the risk of noise-induced hearing loss. Avoiding prolonged exposure to high volumes when using headphones is also important. Maintaining overall health through a balanced diet and regular exercise supports good circulation, which benefits ear function. Staying hydrated and managing stress can also contribute to ear health. Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake can reduce the risk of ear infections and hearing problems. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional ensure early detection and management of any ear-related issues.
Adopting these strategies empowers individuals to protect their hearing and reduce the risk of hearing loss, keeping ears healthy for life.
-
Myths and Truths About Hearing Aids
Myth: Hearing aids restore hearing to normal.
Truth: Hearing aids amplify sounds to improve hearing but do not cure hearing loss or restore hearing to normal levels.Myth: Hearing aids are only for elderly people.
Truth: People of all ages, including children and young adults, can benefit from hearing aids if they have hearing loss.Myth: Hearing aids are bulky and uncomfortable.
Truth: Modern hearing aids are small, lightweight, and designed for comfort and discreet wear.Myth: Hearing aids will make all sounds louder and overwhelming.
Truth: Hearing aids are programmed to amplify specific frequencies and reduce background noise, providing a clearer listening experience.Myth: You don’t need hearing aids if you can hear some sounds.
Truth: Even mild to moderate hearing loss can impact communication and quality of life, and early use of hearing aids can prevent further difficulties.Myth: Hearing aids are too expensive and not worth the investment.
Truth: While hearing aids can be costly, many options and financial assistance programs are available, and the benefits to communication and well-being are significant.Understanding these myths and truths helps individuals make informed decisions about hearing aids and encourages timely intervention for hearing loss.
Safe Listening Practices
Consistently practicing safe listening is key to preventing hearing loss. Recommendations from organizations like the World Health Organization include setting lower volume limits, using noise-canceling headphones instead of turning up the sound, taking breaks from noisy settings, and encouraging children and young adults to adopt these habits early.
Environmental and Occupational Controls
In workplaces, controlling noise at its source can be highly effective. Methods include regular maintenance of machinery, purchasing quieter equipment, using sound dampening materials, and providing thorough training on hearing protection. Fit-testing hearing protectors and conducting regular noise assessments also help ensure workers are protected.
Healthy Habits and Ear Care
Healthy habits play a crucial role in maintaining ear health and preventing hearing loss. Regularly cleaning the ears gently and avoiding the use of sharp objects can prevent damage to the ear canal and eardrum. Protecting ears from loud noises by using earplugs or noise-canceling headphones helps reduce the risk of noise-induced hearing loss. Avoiding prolonged exposure to high volumes when using headphones is also important. Maintaining overall health through a balanced diet and regular exercise supports good circulation, which benefits ear function. Staying hydrated and managing stress can also contribute to ear health. Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake can reduce the risk of ear infections and hearing problems. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional ensure early detection and management of any ear-related issues.
Adopting these strategies empowers individuals to protect their hearing and reduce the risk of hearing loss, keeping ears healthy for life.
-
Myths and Truths About Hearing Aids
Myth: Hearing aids restore hearing to normal.
Truth: Hearing aids amplify sounds to improve hearing but do not cure hearing loss or restore hearing to normal levels.Myth: Hearing aids are only for elderly people.
Truth: People of all ages, including children and young adults, can benefit from hearing aids if they have hearing loss.Myth: Hearing aids are bulky and uncomfortable.
Truth: Modern hearing aids are small, lightweight, and designed for comfort and discreet wear.Myth: Hearing aids will make all sounds louder and overwhelming.
Truth: Hearing aids are programmed to amplify specific frequencies and reduce background noise, providing a clearer listening experience.Myth: You don’t need hearing aids if you can hear some sounds.
Truth: Even mild to moderate hearing loss can impact communication and quality of life, and early use of hearing aids can prevent further difficulties.Myth: Hearing aids are too expensive and not worth the investment.
Truth: While hearing aids can be costly, many options and financial assistance programs are available, and the benefits to communication and well-being are significant.Understanding these myths and truths helps individuals make informed decisions about hearing aids and encourages timely intervention for hearing loss.
Safe Listening Practices
Consistently practicing safe listening is key to preventing hearing loss. Recommendations from organizations like the World Health Organization include setting lower volume limits, using noise-canceling headphones instead of turning up the sound, taking breaks from noisy settings, and encouraging children and young adults to adopt these habits early.
Environmental and Occupational Controls
In workplaces, controlling noise at its source can be highly effective. Methods include regular maintenance of machinery, purchasing quieter equipment, using sound dampening materials, and providing thorough training on hearing protection. Fit-testing hearing protectors and conducting regular noise assessments also help ensure workers are protected.
Healthy Habits and Ear Care
Healthy habits play a crucial role in maintaining ear health and preventing hearing loss. Regularly cleaning the ears gently and avoiding the use of sharp objects can prevent damage to the ear canal and eardrum. Protecting ears from loud noises by using earplugs or noise-canceling headphones helps reduce the risk of noise-induced hearing loss. Avoiding prolonged exposure to high volumes when using headphones is also important. Maintaining overall health through a balanced diet and regular exercise supports good circulation, which benefits ear function. Staying hydrated and managing stress can also contribute to ear health. Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake can reduce the risk of ear infections and hearing problems. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional ensure early detection and management of any ear-related issues.
Adopting these strategies empowers individuals to protect their hearing and reduce the risk of hearing loss, keeping ears healthy for life.
-
Myths and Truths About Hearing Aids
Myth: Hearing aids restore hearing to normal.
Truth: Hearing aids amplify sounds to improve hearing but do not cure hearing loss or restore hearing to normal levels.Myth: Hearing aids are only for elderly people.
Truth: People of all ages, including children and young adults, can benefit from hearing aids if they have hearing loss.Myth: Hearing aids are bulky and uncomfortable.
Truth: Modern hearing aids are small, lightweight, and designed for comfort and discreet wear.Myth: Hearing aids will make all sounds louder and overwhelming.
Truth: Hearing aids are programmed to amplify specific frequencies and reduce background noise, providing a clearer listening experience.Myth: You don’t need hearing aids if you can hear some sounds.
Truth: Even mild to moderate hearing loss can impact communication and quality of life, and early use of hearing aids can prevent further difficulties.Myth: Hearing aids are too expensive and not worth the investment.
Truth: While hearing aids can be costly, many options and financial assistance programs are available, and the benefits to communication and well-being are significant.Understanding these myths and truths helps individuals make informed decisions about hearing aids and encourages timely intervention for hearing loss.
Safe Listening Practices
Consistently practicing safe listening is key to preventing hearing loss. Recommendations from organizations like the World Health Organization include setting lower volume limits, using noise-canceling headphones instead of turning up the sound, taking breaks from noisy settings, and encouraging children and young adults to adopt these habits early.
Environmental and Occupational Controls
In workplaces, controlling noise at its source can be highly effective. Methods include regular maintenance of machinery, purchasing quieter equipment, using sound dampening materials, and providing thorough training on hearing protection. Fit-testing hearing protectors and conducting regular noise assessments also help ensure workers are protected.
Healthy Habits and Ear Care
Healthy habits play a crucial role in maintaining ear health and preventing hearing loss. Regularly cleaning the ears gently and avoiding the use of sharp objects can prevent damage to the ear canal and eardrum. Protecting ears from loud noises by using earplugs or noise-canceling headphones helps reduce the risk of noise-induced hearing loss. Avoiding prolonged exposure to high volumes when using headphones is also important. Maintaining overall health through a balanced diet and regular exercise supports good circulation, which benefits ear function. Staying hydrated and managing stress can also contribute to ear health. Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake can reduce the risk of ear infections and hearing problems. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional ensure early detection and management of any ear-related issues.
Adopting these strategies empowers individuals to protect their hearing and reduce the risk of hearing loss, keeping ears healthy for life.
-
Myths and Truths About Hearing Aids
Myth: Hearing aids restore hearing to normal.
Truth: Hearing aids amplify sounds to improve hearing but do not cure hearing loss or restore hearing to normal levels.Myth: Hearing aids are only for elderly people.
Truth: People of all ages, including children and young adults, can benefit from hearing aids if they have hearing loss.Myth: Hearing aids are bulky and uncomfortable.
Truth: Modern hearing aids are small, lightweight, and designed for comfort and discreet wear.Myth: Hearing aids will make all sounds louder and overwhelming.
Truth: Hearing aids are programmed to amplify specific frequencies and reduce background noise, providing a clearer listening experience.Myth: You don’t need hearing aids if you can hear some sounds.
Truth: Even mild to moderate hearing loss can impact communication and quality of life, and early use of hearing aids can prevent further difficulties.Myth: Hearing aids are too expensive and not worth the investment.
Truth: While hearing aids can be costly, many options and financial assistance programs are available, and the benefits to communication and well-being are significant.Understanding these myths and truths helps individuals make informed decisions about hearing aids and encourages timely intervention for hearing loss.
Safe Listening Practices
Consistently practicing safe listening is key to preventing hearing loss. Recommendations from organizations like the World Health Organization include setting lower volume limits, using noise-canceling headphones instead of turning up the sound, taking breaks from noisy settings, and encouraging children and young adults to adopt these habits early.
Environmental and Occupational Controls
In workplaces, controlling noise at its source can be highly effective. Methods include regular maintenance of machinery, purchasing quieter equipment, using sound dampening materials, and providing thorough training on hearing protection. Fit-testing hearing protectors and conducting regular noise assessments also help ensure workers are protected.
Healthy Habits and Ear Care
Healthy habits play a crucial role in maintaining ear health and preventing hearing loss. Regularly cleaning the ears gently and avoiding the use of sharp objects can prevent damage to the ear canal and eardrum. Protecting ears from loud noises by using earplugs or noise-canceling headphones helps reduce the risk of noise-induced hearing loss. Avoiding prolonged exposure to high volumes when using headphones is also important. Maintaining overall health through a balanced diet and regular exercise supports good circulation, which benefits ear function. Staying hydrated and managing stress can also contribute to ear health. Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake can reduce the risk of ear infections and hearing problems. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional ensure early detection and management of any ear-related issues.
Adopting these strategies empowers individuals to protect their hearing and reduce the risk of hearing loss, keeping ears healthy for life.
-
Myths and Truths About Hearing Aids
Myth: Hearing aids restore hearing to normal.
Truth: Hearing aids amplify sounds to improve hearing but do not cure hearing loss or restore hearing to normal levels.Myth: Hearing aids are only for elderly people.
Truth: People of all ages, including children and young adults, can benefit from hearing aids if they have hearing loss.Myth: Hearing aids are bulky and uncomfortable.
Truth: Modern hearing aids are small, lightweight, and designed for comfort and discreet wear.Myth: Hearing aids will make all sounds louder and overwhelming.
Truth: Hearing aids are programmed to amplify specific frequencies and reduce background noise, providing a clearer listening experience.Myth: You don’t need hearing aids if you can hear some sounds.
Truth: Even mild to moderate hearing loss can impact communication and quality of life, and early use of hearing aids can prevent further difficulties.Myth: Hearing aids are too expensive and not worth the investment.
Truth: While hearing aids can be costly, many options and financial assistance programs are available, and the benefits to communication and well-being are significant.Understanding these myths and truths helps individuals make informed decisions about hearing aids and encourages timely intervention for hearing loss.
Safe Listening Practices
Consistently practicing safe listening is key to preventing hearing loss. Recommendations from organizations like the World Health Organization include setting lower volume limits, using noise-canceling headphones instead of turning up the sound, taking breaks from noisy settings, and encouraging children and young adults to adopt these habits early.
Environmental and Occupational Controls
In workplaces, controlling noise at its source can be highly effective. Methods include regular maintenance of machinery, purchasing quieter equipment, using sound dampening materials, and providing thorough training on hearing protection. Fit-testing hearing protectors and conducting regular noise assessments also help ensure workers are protected.
Healthy Habits and Ear Care
Healthy habits play a crucial role in maintaining ear health and preventing hearing loss. Regularly cleaning the ears gently and avoiding the use of sharp objects can prevent damage to the ear canal and eardrum. Protecting ears from loud noises by using earplugs or noise-canceling headphones helps reduce the risk of noise-induced hearing loss. Avoiding prolonged exposure to high volumes when using headphones is also important. Maintaining overall health through a balanced diet and regular exercise supports good circulation, which benefits ear function. Staying hydrated and managing stress can also contribute to ear health. Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake can reduce the risk of ear infections and hearing problems. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional ensure early detection and management of any ear-related issues.
Adopting these strategies empowers individuals to protect their hearing and reduce the risk of hearing loss, keeping ears healthy for life.
-
Myths and Truths About Hearing Aids
Myth: Hearing aids restore hearing to normal.
Truth: Hearing aids amplify sounds to improve hearing but do not cure hearing loss or restore hearing to normal levels.Myth: Hearing aids are only for elderly people.
Truth: People of all ages, including children and young adults, can benefit from hearing aids if they have hearing loss.Myth: Hearing aids are bulky and uncomfortable.
Truth: Modern hearing aids are small, lightweight, and designed for comfort and discreet wear.Myth: Hearing aids will make all sounds louder and overwhelming.
Truth: Hearing aids are programmed to amplify specific frequencies and reduce background noise, providing a clearer listening experience.Myth: You don’t need hearing aids if you can hear some sounds.
Truth: Even mild to moderate hearing loss can impact communication and quality of life, and early use of hearing aids can prevent further difficulties.Myth: Hearing aids are too expensive and not worth the investment.
Truth: While hearing aids can be costly, many options and financial assistance programs are available, and the benefits to communication and well-being are significant.Understanding these myths and truths helps individuals make informed decisions about hearing aids and encourages timely intervention for hearing loss.
Safe Listening Practices
Consistently practicing safe listening is key to preventing hearing loss. Recommendations from organizations like the World Health Organization include setting lower volume limits, using noise-canceling headphones instead of turning up the sound, taking breaks from noisy settings, and encouraging children and young adults to adopt these habits early.
Environmental and Occupational Controls
In workplaces, controlling noise at its source can be highly effective. Methods include regular maintenance of machinery, purchasing quieter equipment, using sound dampening materials, and providing thorough training on hearing protection. Fit-testing hearing protectors and conducting regular noise assessments also help ensure workers are protected.
Healthy Habits and Ear Care
Healthy habits play a crucial role in maintaining ear health and preventing hearing loss. Regularly cleaning the ears gently and avoiding the use of sharp objects can prevent damage to the ear canal and eardrum. Protecting ears from loud noises by using earplugs or noise-canceling headphones helps reduce the risk of noise-induced hearing loss. Avoiding prolonged exposure to high volumes when using headphones is also important. Maintaining overall health through a balanced diet and regular exercise supports good circulation, which benefits ear function. Staying hydrated and managing stress can also contribute to ear health. Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake can reduce the risk of ear infections and hearing problems. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional ensure early detection and management of any ear-related issues.
Adopting these strategies empowers individuals to protect their hearing and reduce the risk of hearing loss, keeping ears healthy for life.
-
Myths and Truths About Hearing Aids
Myth: Hearing aids restore hearing to normal.
Truth: Hearing aids amplify sounds to improve hearing but do not cure hearing loss or restore hearing to normal levels.Myth: Hearing aids are only for elderly people.
Truth: People of all ages, including children and young adults, can benefit from hearing aids if they have hearing loss.Myth: Hearing aids are bulky and uncomfortable.
Truth: Modern hearing aids are small, lightweight, and designed for comfort and discreet wear.Myth: Hearing aids will make all sounds louder and overwhelming.
Truth: Hearing aids are programmed to amplify specific frequencies and reduce background noise, providing a clearer listening experience.Myth: You don’t need hearing aids if you can hear some sounds.
Truth: Even mild to moderate hearing loss can impact communication and quality of life, and early use of hearing aids can prevent further difficulties.Myth: Hearing aids are too expensive and not worth the investment.
Truth: While hearing aids can be costly, many options and financial assistance programs are available, and the benefits to communication and well-being are significant.Understanding these myths and truths helps individuals make informed decisions about hearing aids and encourages timely intervention for hearing loss.
Safe Listening Practices
Consistently practicing safe listening is key to preventing hearing loss. Recommendations from organizations like the World Health Organization include setting lower volume limits, using noise-canceling headphones instead of turning up the sound, taking breaks from noisy settings, and encouraging children and young adults to adopt these habits early.
Environmental and Occupational Controls
In workplaces, controlling noise at its source can be highly effective. Methods include regular maintenance of machinery, purchasing quieter equipment, using sound dampening materials, and providing thorough training on hearing protection. Fit-testing hearing protectors and conducting regular noise assessments also help ensure workers are protected.
Healthy Habits and Ear Care
Healthy habits play a crucial role in maintaining ear health and preventing hearing loss. Regularly cleaning the ears gently and avoiding the use of sharp objects can prevent damage to the ear canal and eardrum. Protecting ears from loud noises by using earplugs or noise-canceling headphones helps reduce the risk of noise-induced hearing loss. Avoiding prolonged exposure to high volumes when using headphones is also important. Maintaining overall health through a balanced diet and regular exercise supports good circulation, which benefits ear function. Staying hydrated and managing stress can also contribute to ear health. Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake can reduce the risk of ear infections and hearing problems. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional ensure early detection and management of any ear-related issues.
Adopting these strategies empowers individuals to protect their hearing and reduce the risk of hearing loss, keeping ears healthy for life.
-
Myths and Truths About Hearing Aids
Myth: Hearing aids restore hearing to normal.
Truth: Hearing aids amplify sounds to improve hearing but do not cure hearing loss or restore hearing to normal levels.Myth: Hearing aids are only for elderly people.
Truth: People of all ages, including children and young adults, can benefit from hearing aids if they have hearing loss.Myth: Hearing aids are bulky and uncomfortable.
Truth: Modern hearing aids are small, lightweight, and designed for comfort and discreet wear.Myth: Hearing aids will make all sounds louder and overwhelming.
Truth: Hearing aids are programmed to amplify specific frequencies and reduce background noise, providing a clearer listening experience.Myth: You don’t need hearing aids if you can hear some sounds.
Truth: Even mild to moderate hearing loss can impact communication and quality of life, and early use of hearing aids can prevent further difficulties.Myth: Hearing aids are too expensive and not worth the investment.
Truth: While hearing aids can be costly, many options and financial assistance programs are available, and the benefits to communication and well-being are significant.Understanding these myths and truths helps individuals make informed decisions about hearing aids and encourages timely intervention for hearing loss.
Safe Listening Practices
Consistently practicing safe listening is key to preventing hearing loss. Recommendations from organizations like the World Health Organization include setting lower volume limits, using noise-canceling headphones instead of turning up the sound, taking breaks from noisy settings, and encouraging children and young adults to adopt these habits early.
Environmental and Occupational Controls
In workplaces, controlling noise at its source can be highly effective. Methods include regular maintenance of machinery, purchasing quieter equipment, using sound dampening materials, and providing thorough training on hearing protection. Fit-testing hearing protectors and conducting regular noise assessments also help ensure workers are protected.
Healthy Habits and Ear Care
Healthy habits play a crucial role in maintaining ear health and preventing hearing loss. Regularly cleaning the ears gently and avoiding the use of sharp objects can prevent damage to the ear canal and eardrum. Protecting ears from loud noises by using earplugs or noise-canceling headphones helps reduce the risk of noise-induced hearing loss. Avoiding prolonged exposure to high volumes when using headphones is also important. Maintaining overall health through a balanced diet and regular exercise supports good circulation, which benefits ear function. Staying hydrated and managing stress can also contribute to ear health. Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake can reduce the risk of ear infections and hearing problems. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional ensure early detection and management of any ear-related issues.
Adopting these strategies empowers individuals to protect their hearing and reduce the risk of hearing loss, keeping ears healthy for life.
-
Myths and Truths About Hearing Aids
Myth: Hearing aids restore hearing to normal.
Truth: Hearing aids amplify sounds to improve hearing but do not cure hearing loss or restore hearing to normal levels.Myth: Hearing aids are only for elderly people.
Truth: People of all ages, including children and young adults, can benefit from hearing aids if they have hearing loss.Myth: Hearing aids are bulky and uncomfortable.
Truth: Modern hearing aids are small, lightweight, and designed for comfort and discreet wear.Myth: Hearing aids will make all sounds louder and overwhelming.
Truth: Hearing aids are programmed to amplify specific frequencies and reduce background noise, providing a clearer listening experience.Myth: You don’t need hearing aids if you can hear some sounds.
Truth: Even mild to moderate hearing loss can impact communication and quality of life, and early use of hearing aids can prevent further difficulties.Myth: Hearing aids are too expensive and not worth the investment.
Truth: While hearing aids can be costly, many options and financial assistance programs are available, and the benefits to communication and well-being are significant.Understanding these myths and truths helps individuals make informed decisions about hearing aids and encourages timely intervention for hearing loss.
Safe Listening Practices
Consistently practicing safe listening is key to preventing hearing loss. Recommendations from organizations like the World Health Organization include setting lower volume limits, using noise-canceling headphones instead of turning up the sound, taking breaks from noisy settings, and encouraging children and young adults to adopt these habits early.
Environmental and Occupational Controls
In workplaces, controlling noise at its source can be highly effective. Methods include regular maintenance of machinery, purchasing quieter equipment, using sound dampening materials, and providing thorough training on hearing protection. Fit-testing hearing protectors and conducting regular noise assessments also help ensure workers are protected.
Healthy Habits and Ear Care
Healthy habits play a crucial role in maintaining ear health and preventing hearing loss. Regularly cleaning the ears gently and avoiding the use of sharp objects can prevent damage to the ear canal and eardrum. Protecting ears from loud noises by using earplugs or noise-canceling headphones helps reduce the risk of noise-induced hearing loss. Avoiding prolonged exposure to high volumes when using headphones is also important. Maintaining overall health through a balanced diet and regular exercise supports good circulation, which benefits ear function. Staying hydrated and managing stress can also contribute to ear health. Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake can reduce the risk of ear infections and hearing problems. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional ensure early detection and management of any ear-related issues.
Adopting these strategies empowers individuals to protect their hearing and reduce the risk of hearing loss, keeping ears healthy for life.